MAGNETIC FIELD
Today we are going to talk about magnetic fields.
(Suggest more topics in the comment section)
The fundamental problem electrodynamics hopes to solve is this(figure): We have some electric charges, q1,q2,q3,...........(call them source charges); what force do they exert on another charge, Q (call it test charge)?
The position of the source charges are given (as functions of time); the trajectory of the test particle is to be calculated.
 |
| Source charge and test charge |
According to the principle of superposition, it is sufficient to find the force of a single source
charge- the total is then the vector sum of all the individual forces. In the simplest case, electrostatics, the source charge is at rest(though the test charge need not be). We will consider the forces between charges in motion.
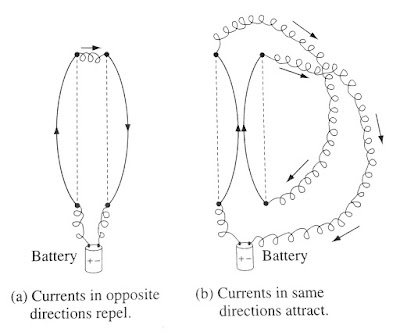
To give you some sense of what is in store, imagine that I set up the following demonstration:
Two wires hang from the ceiling, a few centimetres apart; when I turn on a current, so that it passes up one wire and back down the other, the wires jump apart- they evidently repel one another.
How do we explain this? You might suppose that the battery (or whatever drives the current); is actually charging up the wire, and that force is simply due to the electrical repulsion of like charges. But this is incorrect.
I could hold up a test charge near these wires, and there would be no force(not precisely) it, for the wires are in fact electrically neutral.( It's true that electrons are flowing down the line- that's what a current is- but there are just as many stationary plus charges as moving minus charges on any given segment.) Moreover, if I hook up my demonstration so as to make the current flow up both wires, they are found to attract!
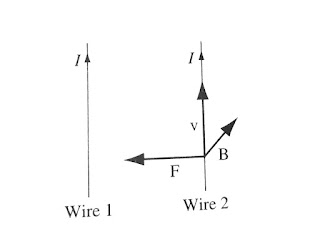
Whatever force accounts for the attraction of parallel currents and the repulsion of antiparallel ones is not electrostatic in nature. It is our first encounter with a magnetic force. Whereas a stationary charge produces only an electric field in the space around it, a moving charge generates, in addition, a magnetic field.
In fact, magnetic fields are a lot easier to detect, in practice---- all you nedd is a compass. How these devices work is irrelevant at the moment; it is enough to know that the needle points in the direction of the local magnetic field.
Ordinarily, this means north, in response to the earth's magnetic field, but in the laboratory, where typical fields may be hundreds of times stronger that that, the compass indicates the direction of whatever magnetic field is present.
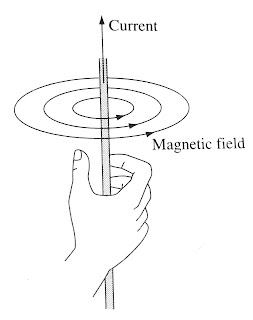
Now if you hold up a tiny compass in the vicinity of a current-carrying wire, you quickly discover a very peculiar thing: The field does not point toward the wire, nor away from it, but rather it circles around the wire. In fact, if you grab the wire with your right hand-thumb in the direction of the current--your fingers curl around in the direction of the magnetic field.
Thanks for reading!!
Please suggest more topics in the comment section.
Subscribe the blog for email notifications.
Or Click here to subscribe-
Or Click here to subscribe-
Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts or suggestions please kindly share.